简易版react-router | 字数总计: 3.4k | 阅读时长: 16分钟 | 阅读量:
学习目标
通过对 react-router 的学习和自己实现其核心功能,更加深度的掌握 react-router 的使用和原理,以达到日常遇到相关问题可以从源码角度快速定位问题并解决问题;(记笔记行为,仅供学习参考,代码解释均在注释里)
react-router 简介
react-router 包含 3 个库,react-router、react-router-dom 和 react-router-native。react-router 提供 最基本的路由功能,实际使用的时候我们不会直接安装 react-router,而是根据应用运行的环境选择安 装 react-router-dom(在浏览器中使用)或 react-router-native(在 rn 中使用)。react-router-dom 和 react-router-native 都依赖 react-router,所以在安装时,react-router 也会自动安装。
使用 demo
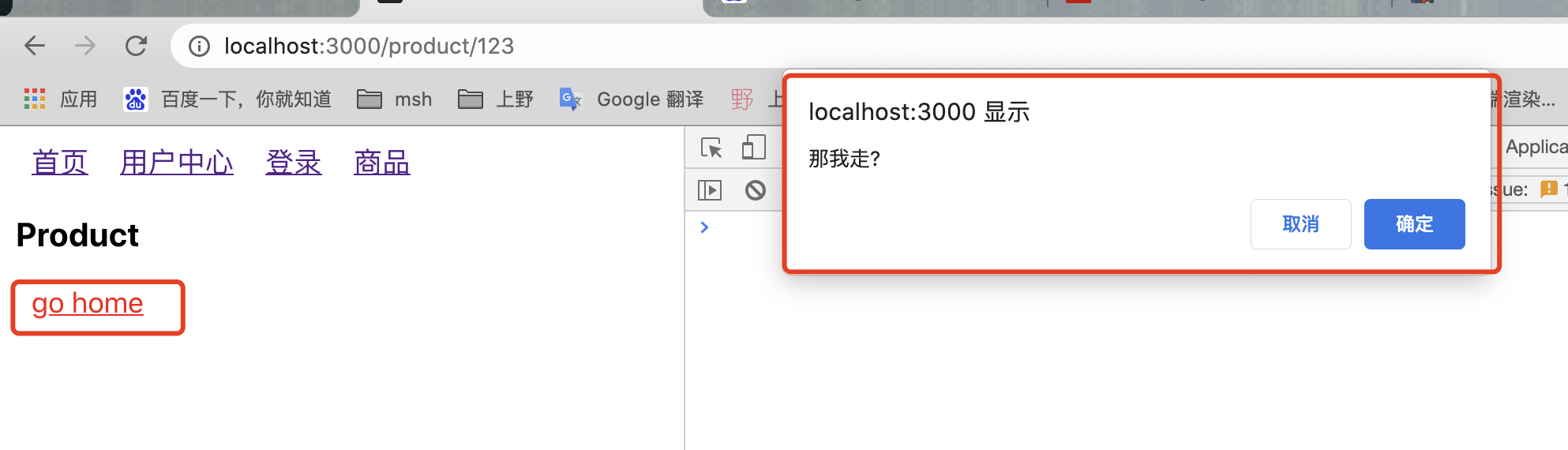
创建HomePage、LoginPage、UserPage、_404Page四个页面; 然后在 App 页面引入并使用,写一个简单的使用例子; 页面效果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 import React , { Component } from 'react' import { BrowserRouter as Router , Route , Link , Switch , useHistory, useLocation, useRouteMatch, useParams, withRouter, Redirect , Prompt , } from './my-router-dom' import HomePage from './pages/HomePage' import UserPage from './pages/UserPage' import LoginPage from './pages/LoginPage' import _404Page from './pages/_404Page' function App ( return ( <div className ="App" > <Router > <Link to ="/" > 首页</Link > <Link to ="/user" > 用户中心</Link > <Link to ="/login" > 登录</Link > <Link to ="/product/123" > 商品</Link > {/*Switch 独占路由: 返回第一个匹配的route或者redirect */} <Switch > {/* children > component > render */} <Route path ="/" exact // children ={children} component ={HomePage} // render ={render} > </Route > <Route path ="/user" exact component ={UserPage} /> <Route path ="/login" exact component ={LoginPage} /> {/* 动态路由 测试 */} <Route path ="/product/:id" component ={Product} // render ={(props) => <Product {...props } /> } /> <Route component ={_404Page} /> </Switch > </Router > </div > ) } export default App @withRouter class Product extends Component { constructor (props ) { super (props) this .state = { confirm : true } } render ( console .log ('Product' , this .props ) return ( <div > <h3 > Product</h3 > <Link to ="/" > go home </Link > {/*测试 Prompt message可以传入字符串,也可以传入函数 */} <Prompt when ={this.state.confirm} message ="那我走?" // message ={(location) => { // return "你确定要离开页面吗"; // }} /> </div > ) } } function Detail ({ match } ) { return ( <div > <h1 > detail</h1 > </div > ) } function children (props ) { console .log ('children props' , props) return <div > children</div > } function render (props ) { console .log ('render props' , props) return <div > render</div > }
实现
BrowserRouter
使用 HTML5 提供的 history API ( pushState , replaceState 和 popstate 事件) 来保持 UI 和 URL 的同步。react-router使用的是 historyAPI 并帮我们抹平了平台差异,可以很放心的使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React from 'react' import { createBrowserHistory } from 'history' import Router from './Router' class BrowserRouter extends React.Component { constructor (props ) { super (props) this .history = createBrowserHistory () } render ( return <Router history ={this.history} children ={this.props.children} /> } } export default BrowserRouter
HashRouter
使用 URL 的 hash 部分(即 window.location.hash )来保持 UI 和 URL 的同步。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import React from 'react' import { createHashHistory } from 'history' import Router from './Router' class BrowserRouter extends React.Component { constructor (props ) { super (props) this .history = createHashHistory () } render ( return <Router history ={this.history} children ={this.props.children} /> } } export default BrowserRouter
Router
Router 组件的作用是将父级的路由模式传给 Switch、Router、Redirect 等子组件,并监听路由变化且刷新页面;
通过Context进行子父组件数据的传递; 通过history.listen监听路由,并在组件卸载时取消监听; location存在state中,利用setState改变值会刷新页面达到重新渲染页面的效果;match是对location.pathname和Route组件配置的path属性做匹配的结果,Router组件中将match设置默认匹配根目录,页面默认首先渲染根目录匹配的组件;其中RouterContext位置在代码在目录 > 其他组件 > RouterContext; 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import React from 'react' import RouterContext from './RouterContext.js' class Router extends React.Component { static computeRootMatch (pathname ) { return { path : '/' , url : '/' , params : {}, isExact : pathname === '/' , } } constructor (props ) { super (props) this .state = { location : props.history .location , } this .unlisten = props.history .listen ((location ) => { this .setState ({ location }) }) } componentWillUnmount ( this .unlisten () } render ( return ( <RouterContext.Provider value ={{ history: this.props.history , location: this.state.location , match: Router.computeRootMatch (this.state.location.pathname ), }} > {this.props.children} </RouterContext.Provider > ) } } export default Router
Route
Route 组件主要作用是对location.pathname和props.path做匹配,如果匹配到就返回match的值,如果没匹配到 match 为 null; 如果path不存在,则 Router 传下来的context.match作为默认值,这样保证 match 存在才能渲染这个没有path的组件,例如 404 页面; Route 组件最重要的是对 children、component、render 三个属性的渲染规则,详细规则写在了代码注释里,请直接看下面的代码; 其中的matchpath是对location和path做匹配的函数,代码在目录 > 其他组件 > matchpath; 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 import React from 'react' import RouterContext from './RouterContext' import matchPath from './matchPath' class Route extends React.Component { constructor (props ) { super (props) } render ( return ( <RouterContext.Consumer > {(context) => { const { location } = context const { path, children, component, render } = this.props // 1.路由的匹配 // Public API for matching a URL pathname to a path. // 404页面没有path 就使用上级传来的默认match const match = path ? matchPath(location.pathname, this.props) : context.match // 传给组件的props router-dom 把history、location等路由的数据传给组件 const props = { ...context, location, match, } console.log('match', match) // 组件的严格匹配 // return match? React.createElement(component) :null // match children > component > render > null // no match : children(function) > null // 详细解析: 1. 先判断match是否存在(存在则找到了路由对应的组件), // 2. 存在的话查找children属性是否存在,如果存在:判断children的类型是否是函数形式,如果是函数形式需要把props传给children,不是函数形式直接渲染children // 3. children不存在:继续找component属性是否存在,component存在就直接通过React.createElement创建组件; // 4. component不存在:查找render属性存不存在,render属性存在就执行render函数并将props传给render,render不存在就直接返回为空; // 5. match如果不存在,渲染函数子组件 // 由于context的取值规则是 取到最近一层的provide传进来的值 // 这里再包一层 <RouterContext.Provider是为了写hook useRouteMatch的时候,route可以拿到当前匹配的match传给组件,不传这一层,组件拿到的match就会是最顶级router(browserRouter/hashRouter)传来的默认match return ( <RouterContext.Provider value ={props} > {match ? children ? typeof children === 'function' ? children(props) : children : component ? React.createElement(component, props) : render ? render(props) : null : typeof children === 'function' ? children(props) : null} </RouterContext.Provider > ) }} </RouterContext.Consumer > ) } } export default Route
Link
Link.js: 跳转链接,处理点击事件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import React , { useContext } from 'react' import RouterContext from './RouterContext' function Link ({ to, children , ...rest} ) { const context = useContext (RouterContext ) const handleClick = (e ) => { e.preventDefault () context.history .push (to) } return ( <a href ={to} onClick ={handleClick} {...rest }> {children} </a > ) } export default Link
Switch
Switch组件的主要作用是独占路由,保证当前页面只渲染 match 匹配的一个组件; 不加Switch组件,Route组件的 children 属性渲染层级比较高,则都会被渲染; Switch中对子组件进行循环匹配,如果找到match则通过React.cloneElement渲染对应组件,没有匹配就渲染404页面(假设Route配置了404页面); 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 import React from 'react' import RouterContext from './RouterContext' import matchpath from './matchPath' class Switch extends React.Component { render ( return ( <RouterContext.Consumer > {(context) => { const location = context.location // 记录是否匹配 let match // 记录匹配的元素(route/redirect) let element // 利用 React.Children 对switch的子组件route们遍历 React.Children.forEach(this.props.children, (child) => { // match为 null 证明还没匹配上,且child是有效的元素 if (match == null && React.isValidElement(child)) { // 缓存组件 element = child // 判断route是否存在path 如果存在就拿到path去和当前location的path做对比,不存在就使用祖传的默认match match = child.props.path ? matchpath(location.pathname, child.props) : context.match } }) return match ? React.cloneElement(element, { computedMatch: match }) : null }} </RouterContext.Consumer > ) } } export default Switch
Redirect
Redirect组件作用是对路由进行重定向
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import React from 'react' import RouterContext from './RouterContext' import LifeCycle from './LifeCycle' class Redirect extends React.Component { render ( return ( <RouterContext.Consumer > {(context) => { const { history } = context const { to, push = false } = this.props return ( <LifeCycle onMount ={() => { push ? history.push(to) : history.replace(to) }} /> ) }} </RouterContext.Consumer > ) } } export default Redirect
hooks
hooks组件主要作用是给函数组件提供路由hook,确保在函数组中可以使用路由的history、location等一众属性和方法;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import { useContext } from 'react' import RouterContext from './RouterContext' export function useHistory ( return useContext (RouterContext ).history } export function useLocation ( return useContext (RouterContext ).location } export function useRouteMatch ( return useContext (RouterContext ).match } export function useParams ( const match = useContext (RouterContext ).match return match ? match.params : null }
Prompt
Prompt组件主要作用是对路由离开之前进行提示;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 import React from 'react' import RouterContext from './RouterContext' import LifeCycle from './LifeCycle' class Prompt extends React.Component { render ( return ( <RouterContext.Consumer > {(context) => { const { message, when = true } = this.props if (!when) return null // 利用history库的 block 在离开页面的时候做拦截 const method = context.history.block // const return ( <LifeCycle onMount ={(self) => { // 组件挂载的时候把 method 存在 release上 self.release = method(message) }} onUpdate={(self, prevProps) => { if (prevProps.message !== message) { self.release() self.release = method(message) } }} onUnmount={(self) => { self.release() }} message={message} /> ) }} </RouterContext.Consumer > ) } } export default Prompt
WithRouter
withRouter本身是一个hoc高级组件,为类组件提供history的方法;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import RouterContext from './RouterContext' const withRouter = (WrapperComponent ) => (props ) => { return ( <RouterContext.Consumer > {(context) => <WrapperComponent {...props } {...context } /> } </RouterContext.Consumer > ) } export default withRouter
MemoryRouter
MemoryRouter直接拷贝的 react-router 源码, MemoryRouter一般写native会用到,web的话常用BrowserRouter和HashRouter;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 import React from 'react' import PropTypes from 'prop-types' import { createMemoryHistory as createHistory } from 'history' import warning from 'tiny-warning' import Router from './Router.js' class MemoryRouter extends React.Component { history = createHistory (this .props ) render ( return <Router history ={this.history} children ={this.props.children} /> } } if (__DEV__) { MemoryRouter .propTypes = { initialEntries : PropTypes .array , initialIndex : PropTypes .number , getUserConfirmation : PropTypes .func , keyLength : PropTypes .number , children : PropTypes .node , } MemoryRouter .prototype componentDidMount = function ( warning ( !this .props .history , '<MemoryRouter> ignores the history prop. To use a custom history, ' + 'use `import { Router }` instead of `import { MemoryRouter as Router }`.' ) } } export default MemoryRouter
其他组件
RouterContext
1 2 3 4 5 6 import React from 'react' const RouterContext = React .createContext ()export default RouterContext
LifeCycle
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 import React from 'react' class LifeCycle extends React.Component { componentWillMount ( if (this .props .onMount ) this .props .onMount .call (this , this ) } componentWillUpdate (prevProps ) { if (this .props .onUpdate ) this .props .onUpdate .call (this , this , prevProps) } componentWillUnmount ( if (this .props .onUnmount ) this .props .onUnmount .call (this , this ) } render ( return null } } export default LifeCycle
matchpath
path-to-regexp这个库真的蛮好用的,github 、Express Route Tester ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 import pathToRegexp from 'path-to-regexp' const cache = {}const cacheLimit = 10000 let cacheCount = 0 function compilePath (path, options ) { const cacheKey = `${options.end} ${options.strict} ${options.sensitive} ` const pathCache = cache[cacheKey] || (cache[cacheKey] = {}) if (pathCache[path]) return pathCache[path] const keys = [] const regexp = pathToRegexp (path, keys, options) const result = { regexp, keys } if (cacheCount < cacheLimit) { pathCache[path] = result cacheCount++ } return result } function matchPath (pathname, options = {} ) { if (typeof options === 'string' || Array .isArray (options)) { options = { path : options } } const { path, exact = false , strict = false , sensitive = false } = options const paths = [].concat (path) return paths.reduce ((matched, path ) => { if (!path && path !== '' ) return null if (matched) return matched const { regexp, keys } = compilePath (path, { end : exact, strict, sensitive, }) const match = regexp.exec (pathname) if (!match) return null const [url, ...values] = match const isExact = pathname === url if (exact && !isExact) return null return { path, url : path === '/' && url === '' ? '/' : url, isExact, params : keys.reduce ((memo, key, index ) => { memo[key.name ] = values[index] return memo }, {}), } }, null ) } export default matchPath